Art of Electronics 2nd edition, pages 2-4
Overview
Voltage & Current describe two aspects of electronic circuits that are fundamental to understand and on which everything else will build on.
What you MUST learn
Voltage refers to a force that when applied across a circuit causes current to flow. Voltage is measured in volts (using the symbol V) also called a “potential difference”. It is measured across two points in a circuit. A joule of work is needed to move a coulomb of charge through a potential difference of one volt. A coulomb is the charge of about 6×10^18 electrons.
Current (symbol: I) is the measure of electronics through a point in a circuit. It is measured in amperes (amps) (symbol: A). 1 ampere (amp) is 1 coulomb of charge passing through a point per second.
Conservation of Charge: Kirchhoff’s current law
The sum of currents into a point or node is equal to the sum of the currents out of a point or node. This is referred to as Kirchhoff’s current law.
Kirchhoff’s voltage law
The sum of voltage drops through one branch of a circuit will equal the sum of voltage drops across the other branches of the circuit.
P=VI
Power (work per unit time), measured in watts. (1 W = 1 J/s)
P=VI = (work/charge) x (charge/time) = work/time
P=VI= (1 joules/1 coulomb) x (1 coulomb/1 second) = 1 joules/second = watt.
Things good to learn
Voltage is usually written with the symbol V but sometimes E is used. Voltage is also called a “potential difference” or electromotive force (EMF).
Prefixes:
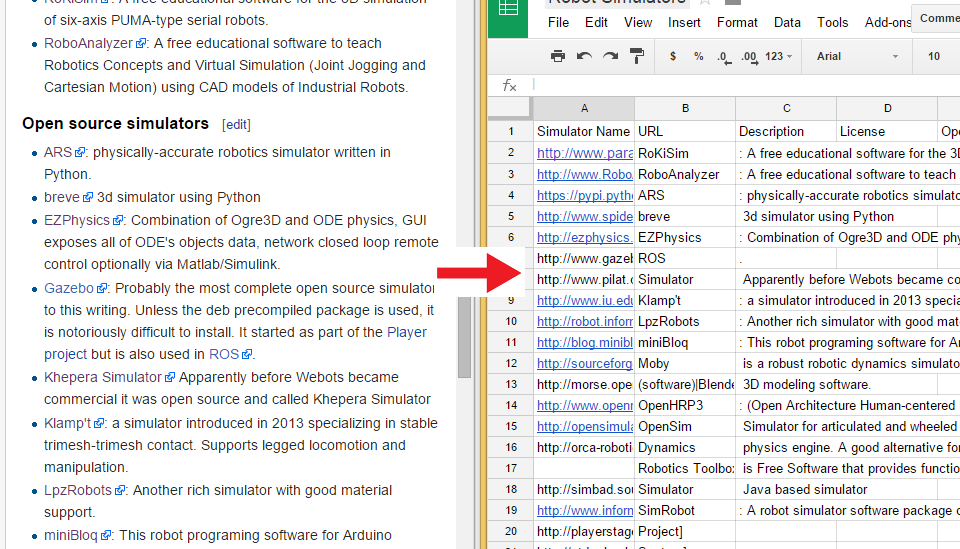
| Multiple | Prefix | Symbol |
| 10^12 | tera | T |
| 10^9 | giga | G |
| 10^6 | mega | M |
| 10^3 | kilo | k |
| 10^(-3) | milli | m |
| 10^(-6) | micro | µ |
| 10^(-9) | nano | n |
| 10^(-12) | pico | p |
| 10^(-15) | femto | f |
When abbreviating a unit with a prefix, the unit follows the multiplier with no space and the unit is capitalized. However, no capitalization for both prefix and unit when spelled out. 1mW = 1 milliwatt
1 MV = 1 megavolt
Related information and insights from my other books
Introductory Circuit Analysis 9th edition – chapter 2
Structure of the atom:
nucleus is made up of protons (that have a positive charge) and neutrons that have a negative charge. The proton and neutron are relatively the same mass. But the electron is considerably smaller (1836 times smaller) than the proton but has a negative charge that is equal to the positive charge of the proton.
Other things of interest
If you need more help
Voltage
Current
Joule
If you wanted to know
Who defined:
Voltage
Volt
Current
amp
joule
watt
multiplier prefixes
People who contributed:
Watt
Power Point:
GadgetNateJourneyThroughArtOfElectronics-01.01-VoltageAndCurrent


 We have been slowly collecting tablets in the form of iPad (original), iPad mini, HP slates, and recently through a purchase of 2 RCA slates that we got for $65 from Walmart during the most recent black Friday sale.
We have been slowly collecting tablets in the form of iPad (original), iPad mini, HP slates, and recently through a purchase of 2 RCA slates that we got for $65 from Walmart during the most recent black Friday sale.


 “The Art of Electronics” by Horowitz and Hill
“The Art of Electronics” by Horowitz and Hill
 Since the Spring of this year, I have met more authors that I knew in Exeter, NH then I have in all the rest of my life combined. These have been arranged by the
Since the Spring of this year, I have met more authors that I knew in Exeter, NH then I have in all the rest of my life combined. These have been arranged by the  reate a chapter by chapter outline (usually about 40 chapters). At this point production really gets into gear and he writes one chapter a day. In about 6-8 weeks he has the first draft of his book. He then sends this off to the editor and even after publishing millions of copies of books, he anxiously awaits the feedback. Then he gets it back with comments. Reworks a bit of it. And sends it back. “The keys,” he says, ” is to plan.”
reate a chapter by chapter outline (usually about 40 chapters). At this point production really gets into gear and he writes one chapter a day. In about 6-8 weeks he has the first draft of his book. He then sends this off to the editor and even after publishing millions of copies of books, he anxiously awaits the feedback. Then he gets it back with comments. Reworks a bit of it. And sends it back. “The keys,” he says, ” is to plan.” And now we are even more glad we did.
And now we are even more glad we did.